Zero-Based Organisation (ZBO) concepts, much like Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB), are powerful tools for enhancing efficiency, controlling costs, and aligning strategy across various business contexts. Implementing these approaches can be crucial during crisis management, restructuring, post-merger integration, expansion phases, and broader efficiency programs.
In times of crisis, every decision can have a profound impact on an organisation’s ability to survive and recover. Zero-Based Organisation and Budgeting offer a powerful approach for rapid resource optimisation. These methodologies enable organisations to efficiently allocate resources by designing the organisational structure and starting each budgeting cycle from a ‘zero-base’.
This approach marks a significant departure from traditional management practices, which often build upon existing scenarios and can perpetuate historical inefficiencies. Instead, the Zero-Based mindset requires a thorough re-evaluation of resources and expenditures, compelling organisations to justify how every dollar spent aligns with their strategic goals. This rigorous process is essential for identifying non-essential expenses and investments, leading to substantial reductions in operational and capital expenditures
Understanding Crisis Scenarios
Crisis scenarios can vary widely across industries but are primarily caused by complications in financial management, operation disruptions and strategy challenges:
- Financials: Inability to pay debts, cash flow issues (e.g., mismanagement of the cash conversion cycle and customer defaults), and other external economic factors, such as a drop in commodity prices reducing revenue and profitability.
- Operations: Difficulties in rationalising administrative and operational costs, as raw material and workforce costs, and unexpected events like the COVID-19 pandemic and natural disasters (earthquakes, floods, hurricanes)
- Strategy: Unsuccessful M&A, new product or market failures, and competitive pressure.
A quick resources optimisation is crucial for businesses going through similar scenarios. One advantage of applying Zero-Based Organisation and Budgeting is that it can help evaluate the current structure, projects and running costs are in line with revised strategic goals, focusing resources on the most promising initiatives and core activities.
Visagio’s Methodology for Quick Resource Optimisation
Visagio`s methodology for quick resource optimisation starts with an assessment of current spending patterns by mapping all processes, projects, contracts and other resources present in the company forecast to define what are the main drivers we should be considering giving the new scenario of the organisation.
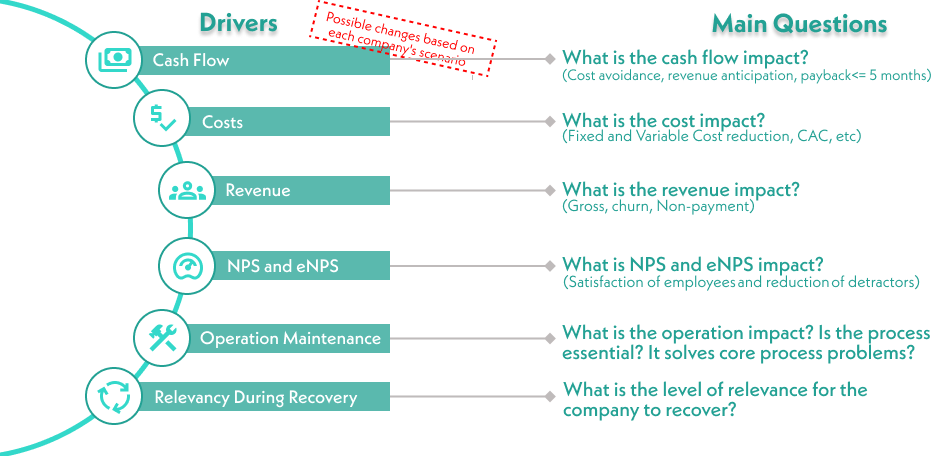

Afterwards, an analysis is conducted to determine each item’s relevance to the business by evaluating the magnitude of its impact on the main pillars of a decision such as cash flow, costs, revenue, NPS, eNPS, and operational continuity.
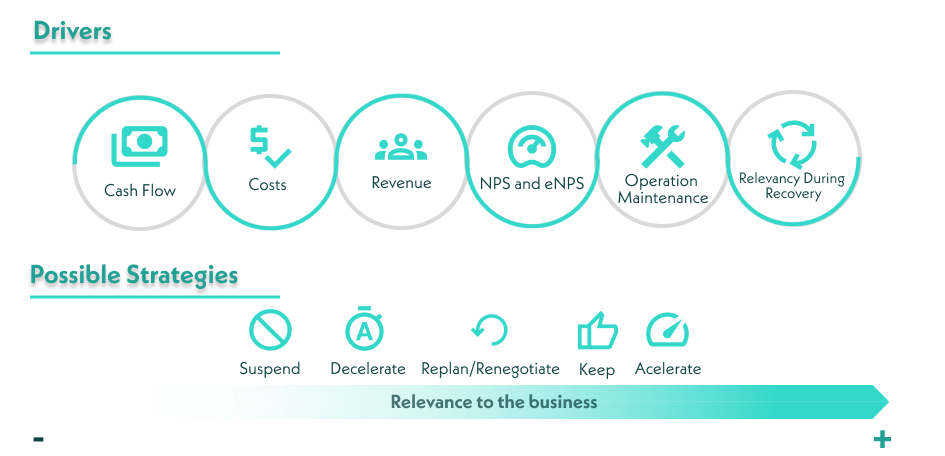

A final recommendation is compiled, containing actions for each budget item and an estimation of the financial impact expected from these decisions. The decisions include suspending (e.g., immediately suspending spending on R&D and projects without immediate payback), slowing down, replanning, maintaining, or accelerating (e.g., accelerating projects that improve cash flow).
Once decisions are made and the company has a clear roadmap of actions, it is essential to monitor and ensure implementation by integrating the plan into the company forecast and tracking actuals.
Proven Success
Visagio’s experience has shown that efficiency and business continuity are mainly achieved by:
- Cutting all non-essential costs
- Renegotiating contracts
- Stopping investments and hiring, re-evaluating all initiatives with a focus on those with immediate payback
- Reducing all expenses, including bonuses and extra remuneration
- Controlling cash on a daily basis, focusing on liquidity and anticipating receivables
- Structuring cash to withstand the most adverse scenarios, forecasting zero revenue
The application of this methodology in a telecom company resulted in a reduction of more than AUD 26 million in OPEX and over AUD 8 million in CAPEX, in addition to aligning the company’s efforts to thrive in a new market context. This outcome was achieved through an exhaustive review of over 800 initiatives and projects, spanning more than 10 directorates within the company.


Critical Success Factors
There are critical success factors when implementing this methodology. It is important to involve finance as a strategic partner starting from the assessment until ongoing monitoring of the results. No time can be lost during a crisis, so agile decision-making and a clear sense of prioritisation are indispensable. ZBB implementation affects cross-functional stakeholders, so strong leadership, unified organisational objectives, and a transparent communication plan are necessary.
Conclusion
Zero-Based Organisation and Budgeting offer a crucial methodology for resource optimization enabling organisations to thoroughly reassess and reallocate their resources. By starting from a zero base, companies can pinpoint and eliminate non-essential expenditures, focusing on initiatives and activities that provide immediate value. This approach not only drives significant cost reductions but also aligns spending with strategic priorities, ensuring long-term stability and growth. The telecom sector case study demonstrates how this strategy can lead to substantial financial and operational improvements, making it a vital approach for businesses looking to succeed.
Curious about uncovering hidden opportunities within your organisation? Connect with Visagio to learn how we can help identify and maximise value through tailored business transformation strategies. Message us at contact@visagio.com.
About the author
Renan Momesso is a Management Consultant at Visagio with extensive experience in implementation projects, developing and applying solutions in various areas such as post-merger integration, global services provider, procurement, financial modelling and customer experience. He has worked across a broad range of industry sectors, including mining, financial services, technology and the not-for-profit sector.


